《跟我学Shiro》笔记02-身份验证
原文地址:第二章 身份验证——《跟我学Shiro》
目录贴: 跟我学Shiro目录贴
源码:https://github.com/zhangkaitao/shiro-example
身份验证
身份验证,即在应用中谁能证明他就是他本人。一般提供如他们的身份ID一些标识信息来表明他就是他本人,如提供身份证,用户名/密码来证明。
在 shiro 中,用户需要提供 principals(身份)和 credentials(证明)给 shiro,从而应用能验证用户身份:
principals:身份,即主体的标识属性,可以是任何东西,如用户名、邮箱等,唯一即可。一个主体可以有多个principals,但只有一个 Primary principals,一般是用户名/密码/手机号。
credentials:证明/凭证,即只有主体知道的安全值,如密码/数字证书等。
最常见的 principals 和 credentials 组合就是用户名/密码了。接下来先进行一个基本的身份认证。
另外两个相关的概念是之前提到的 Subject 及 Realm,分别是主体及验证主体的数据源。
环境准备
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>登录/退出
1、首先准备一些用户身份/凭据(shiro.ini)
[users]
zhang=123
wang=123此处使用 ini 配置文件,通过 [users] 指定了两个主体:zhang/123、wang/123。
2、测试用例(com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.LoginLogoutTest)
@Test
public void testHelloworld() {
// 1、获取 SecurityManager 工厂,此处使用 Ini 配置文件初始化 SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
// 2、得到 SecurityManager 实例 并绑定给 SecurityUtils,这是一个全局设置,设置一次即可
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 3、通过 SecurityUtils 得到 Subject,其会自动绑定到当前线程;如果在 web 环境在请求结束时需要解除绑定;
// 得到 Subject 及创建用户名/密码身份验证 Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhang", "123");
try {
// 4、调用 subject.login 方法进行登录,其会自动委托给 SecurityManager.login 方法进行登录,即身份验证
subject.login(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
// 5、身份验证失败
/*
如果身份验证失败请捕获AuthenticationException或其子类,常见的如:
DisabledAccountException(禁用的帐号)
LockedAccountException(锁定的帐号)
UnknownAccountException(错误的帐号)
ExcessiveAttemptsException(登录失败次数过多)
IncorrectCredentialsException (错误的凭证)
ExpiredCredentialsException(过期的凭证)
等,具体请查看其继承关系;
*/
}
Assert.assertEquals(true, subject.isAuthenticated()); // 断言用户已经登录
// 6、退出,其会自动委托给SecurityManager.logout方法退出
subject.logout();
}身份认证流程
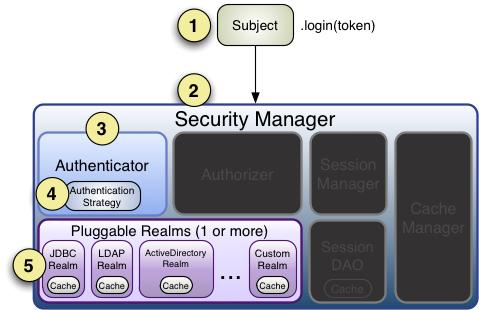
流程如下:
首先调用
Subject.login(token)进行登录,其会自动委托给SecurityManager,调用之前必须通过SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager()设置;SecurityManager负责真正的身份验证逻辑;它会委托给Authenticator进行身份验证;Authenticator才是真正的身份验证者,Shiro API 中核心的身份认证入口点,此处可以自定义插入自己的实现;Authenticator可能会委托给相应的AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证,默认ModularRealmAuthenticator会调用AuthenticationStrategy进行多Realm身份验证;Authenticator会把相应的token传入Realm,从Realm获取身份验证信息,如果没有返回/抛出异常表示身份验证失败了。此处可以配置多个Realm,将按照相应的顺序及策略进行访问。
Realm
Realm:域,Shiro 从 Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm 得到用户相应的角色/权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把 Realm 看成 DataSource,即安全数据源。如我们之前的 ini 配置方式将使用 org.apache.shiro.realm.text.IniRealm。
自定义Realm实现
// com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm1
public class MyRealm1 implements Realm {
// 返回一个唯一的 Realm 名字
@Override
public String getName() {
return "myrealm1";
}
// 判断此 Realm 是否支持此 Token
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
// 仅支持 UsernamePasswordToken 类型的 Token
return token instanceof UsernamePasswordToken;
}
// 根据 Token 获取认证信息
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); // 得到用户名
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials()); // 得到密码
if(!"zhang".equals(username)) {
throw new UnknownAccountException(); // 如果用户名错误
}
if(!"123".equals(password)) {
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(); // 如果密码错误
}
// 如果身份认证验证成功,返回一个 AuthenticationInfo 实现;
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username, password, getName());
}
}ini 配置文件指定自定义 Realm 实现(shiro-realm.ini)
[main]
; 声明一个 realm
myRealm1=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm1
; 指定 securityManager 的 realms 实现,通过 $name 来引入之前的 realm 定义
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1测试用例请参考 com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.LoginLogoutTest 的 testCustomRealm 测试方法,只需要把之前的 shiro.ini 配置文件改成 shiro-realm.ini 即可
多 Realm 配置
ini 配置文件(shiro-multi-realm.ini)
[main]
; 声明一个 realm
myRealm1=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm1
myRealm2=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm2
; 指定 securityManager 的 realms 实现
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm2securityManager 会按照 realms 指定的顺序进行身份认证。此处我们使用显示指定顺序的方式指定了 Realm 的顺序,如果删除 securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm2,那么 securityManager 会按照 realm 声明的顺序进行使用 (即无需设置 realms 属性,其会自动发现),当我们显示指定 realm 后,其他没有指定 realm 将被忽略,如securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,那么 myRealm2 不会被自动设置进去。
Shiro 默认提供的 Realm
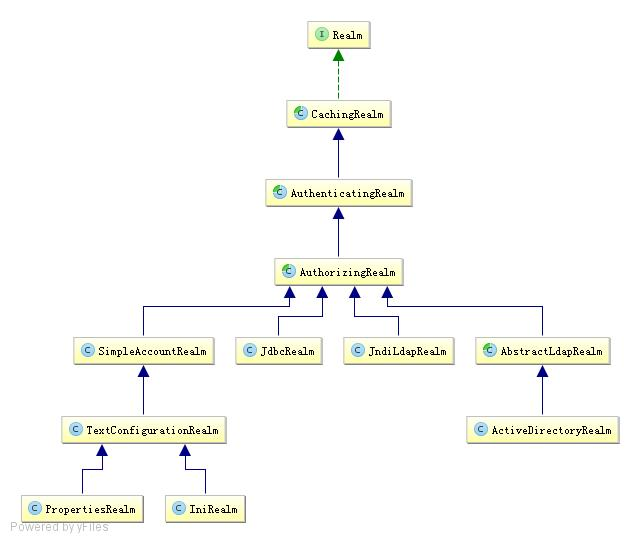
一般继承 AuthorizingRealm(授权)即可;其继承了 AuthenticatingRealm(即身份验证),而且也间接继承了 CachingRealm(带有缓存实现)。其中主要默认实现如下:
org.apache.shiro.realm.text.IniRealm:[users] 部分指定用户名/密码及其角色;[roles] 部分指定角色即权限信息;
org.apache.shiro.realm.text.PropertiesRealm: user.username=password,role1,role2 指定用户名/密码及其角色;role.role1=permission1,permission2 指定角色及权限信息;
org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm:通过 sql 查询相应的信息,如 select password from users where username = ? 获取用户密码, select password, password_salt from users where username = ? 获取用户密码及盐; select role_name from user_roles where username = ? 获取用户角色; select permission from roles_permissions where role_name = ? 获取角色对应的权限信息;也可以调用相应的 api 进行自定义 sql;
JDBC Realm 使用
本文将使用 mysql 数据库及 druid 连接池。
maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.11</version>
</dependency>创建数据库表
到数据库shiro下建三张表:users(用户名/密码)、user_roles(用户/角色)、roles_permissions(角色/权限),并添加一个用户记录,用户名/密码为zhang/123;
drop database if exists shiro;
create database shiro;
use shiro;
create table users (
id bigint auto_increment,
username varchar(100),
password varchar(128),
password_salt varchar(100),
constraint pk_users primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_users_username on users(username);
create table user_roles(
id bigint auto_increment,
username varchar(100),
role_name varchar(100),
constraint pk_user_roles primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_user_roles on user_roles(username, role_name);
create table roles_permissions(
id bigint auto_increment,
role_name varchar(100),
permission varchar(100),
constraint pk_roles_permissions primary key(id)
) charset=utf8 ENGINE=InnoDB;
create unique index idx_roles_permissions on roles_permissions(role_name, permission);
insert into users(username,password)values('zhang','123');ini 配置(shiro-jdbc-realm.ini)
[main]
jdbcRealm=org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm
dataSource=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
dataSource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
dataSource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/shiro
dataSource.username=root
dataSource.password=123
jdbcRealm.dataSource=$dataSource
securityManager.realms=$jdbcRealm变量名=全限定类名会自动创建一个类实例
变量名.属性=值 自动调用相应的setter方法进行赋值
$变量名 引用之前的一个对象实例
测试代码请参照 com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.LoginLogoutTest 的 testJDBCRealm 方法,和之前的没什么区别(只用修改 ini 配置文件)。
Authenticator 及 AuthenticationStrategy
Authenticator 的职责是验证用户帐号,是 Shiro API 中身份验证核心的入口点:
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException;如果验证成功,将返回 AuthenticationInfo 验证信息;此信息中包含了身份及凭证;如果验证失败将抛出相应的 AuthenticationException 实现。
AuthenticationStrategy 默认实现
SecurityManager 接口继承了 Authenticator,另外还有一个 ModularRealmAuthenticator 实现,其委托给多个 Realm 进行验证,验证规则通过 AuthenticationStrategy 接口指定,默认提供的实现:
FirstSuccessfulStrategy:只要有一个Realm验证成功即可,只返回第一个Realm身份验证成功的认证信息,其他的忽略;AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy:只要有一个Realm验证成功即可,和FirstSuccessfulStrategy不同,返回所有Realm身份验证成功的认证信息;AllSuccessfulStrategy:所有Realm验证成功才算成功,且返回所有Realm身份验证成功的认证信息,如果有一个失败就失败了。
ModularRealmAuthenticator 默认使用 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy 策略。
测试 AuthenticationStrategy 默认实现
三个 realm
- myRealm1:用户名/密码为 zhang/123 时成功,且返回身份/凭据为 zhang/123;(代码见上文)
- myRealm2:用户名/密码为 wang/123 时成功,且返回身份/凭据为 wang/123(代码将上文的 'zhang' 修改为 'wang');
- myRealm3:用户名/密码为 zhang/123 时成功,且返回身份/凭据为 zhang@163.com/123,和 myRealm1 不同的是返回时的身份变了;
// com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.myRealm3
public class MyRealm3 implements Realm {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "myrealm3";
}
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token instanceof UsernamePasswordToken; // 仅支持 UsernamePasswordToken 类型的 Token
}
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = (String)token.getPrincipal(); // 得到用户名
String password = new String((char[])token.getCredentials()); // 得到密码
if(!"zhang".equals(username)) {
throw new UnknownAccountException(); // 如果用户名错误
}
if(!"123".equals(password)) {
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(); // 如果密码错误
}
// 如果身份认证验证成功,返回一个 AuthenticationInfo 实现;
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(username + "@163.com", password, getName());
}
}ini 配置文件
shiro-authenticator-all-success.ini
[main]
; 指定 securityManager的authenticator 实现
authenticator=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator
securityManager.authenticator=$authenticator
; 指定 securityManager.authenticator 的 authenticationStrategy
allSuccessfulStrategy=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AllSuccessfulStrategy
securityManager.authenticator.authenticationStrategy=$allSuccessfulStrategy
myRealm1=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm1
myRealm2=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm2
myRealm3=com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.realm.MyRealm3
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm3
; shiro-authenticator-all-fail.ini,这个修改 securityManager.realms
; securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm2首先通用化登录逻辑
// com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.AuthenticatorTest
private void login(String configFile) {
// 1、获取 SecurityManager 工厂,此处使用 Ini 配置文件初始化 SecurityManager
Factory<org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager> factory =
new IniSecurityManagerFactory(configFile);
// 2、得到 SecurityManager 实例 并绑定给 SecurityUtils
org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 3、得到 Subject 及创建用户名/密码身份验证 Token(即用户身份/凭证)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("zhang", "123");
subject.login(token);
}测试 AllSuccessfulStrategy 成功
@Test
public void testAllSuccessfulStrategyWithSuccess() {
login("classpath:shiro-authenticator-all-success.ini");
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 得到一个身份集合,其包含了 Realm 验证成功的身份信息
PrincipalCollection principalCollection = subject.getPrincipals();
Assert.assertEquals(2, principalCollection.asList().size());
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
ThreadContext.unbindSubject(); // 退出时请解除绑定 Subject 到线程 否则对下次测试造成影响
}测试 AllSuccessfulStrategy 失败
@Test(expected = UnknownAccountException.class)
public void testAllSuccessfulStrategyWithFail() {
login("classpath:shiro-authenticator-all-fail.ini");
}测试 AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy 成功
; 修改上文 ini 配置文件中
allSuccessfulStrategy=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm2,$myRealm3@Test
public void testAtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategyWithSuccess() {
login("classpath:shiro-authenticator-atLeastOne-success.ini");
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 得到一个身份集合,其包含了所有 Realm 验证成功的身份信息
PrincipalCollection principalCollection = subject.getPrincipals();
Assert.assertEquals(2, principalCollection.asList().size());
}测试 FirstSuccessfulStrategy 成功
; 修改上文 ini 配置文件中
allSuccessfulStrategy=org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.FirstSuccessfulStrategy
securityManager.realms=$myRealm1,$myRealm2,$myRealm3@Test
public void testFirstOneSuccessfulStrategyWithSuccess() {
login("classpath:shiro-authenticator-first-success.ini");
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 得到一个身份集合,其包含了第一个 Realm 验证成功的身份信息
PrincipalCollection principalCollection = subject.getPrincipals();
Assert.assertEquals(1, principalCollection.asList().size());
}自定义 AuthenticationStrategy 实现
自定义实现时一般继承 org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AbstractAuthenticationStrategy 即可。
只能有一个 Realm 验证成功
// com.github.zhangkaitao.shiro.chapter2.authenticator.strategy.OnlyOneAuthenticatorStrategy
public class OnlyOneAuthenticatorStrategy extends AbstractAuthenticationStrategy {
// 在所有 Realm 验证之前调用
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAllAttempts(Collection<? extends Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(); // 返回一个权限的认证信息
}
// 在每个 Realm 之前调用
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo beforeAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException {
return aggregate; // 返回之前合并的
}
// 在每个 Realm 之后调用
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAttempt(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo singleRealmInfo, AuthenticationInfo aggregateInfo, Throwable t) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info;
if (singleRealmInfo == null) {
info = aggregateInfo;
} else {
if (aggregateInfo == null) {
info = singleRealmInfo;
} else {
info = merge(singleRealmInfo, aggregateInfo); // 合并
if(info.getPrincipals().getRealmNames().size() > 1) {
System.out.println(info.getPrincipals().getRealmNames());
throw new AuthenticationException("Authentication token of type [" + token.getClass() + "] " +
"could not be authenticated by any configured realms. Please ensure that only one realm can " +
"authenticate these tokens.");
}
}
}
return info;
}
// 在所有 Realm 之后调用
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo afterAllAttempts(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo aggregate) throws AuthenticationException {
return aggregate;
}
}转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 bin07280@qq.com
文章标题:《跟我学Shiro》笔记02-身份验证
文章字数:3.2k
本文作者:Bin
发布时间:2018-04-09, 21:12:22
最后更新:2019-08-31, 21:59:52
原始链接:http://coolview.github.io/2018/04/09/%E8%B7%9F%E6%88%91%E5%AD%A6Shiro/%E3%80%8A%E8%B7%9F%E6%88%91%E5%AD%A6Shiro%E3%80%8B%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B002-%E8%BA%AB%E4%BB%BD%E9%AA%8C%E8%AF%81/版权声明: "署名-非商用-相同方式共享 4.0" 转载请保留原文链接及作者。